R&D Management Division
Research & Development Unit
YANMAR Technical Review
Secure File Exchange System for Improving the Speed of Research and Development (cnct-partner)
Abstract
Use of computer networks is essential to business.
Yanmar also uses computer networks to expedite collaboration with external partners.
To meet the greater demand this creates for secure file exchange, Yanmar has created a new secure file exchange system called cnct-partner.
1. Introduction
Information sharing at Yanmar
The sharing of information via computer networks has become essential to business. To expedite research and development (R&D), Yanmar is also making greater use of external partners, including through collaborations, outsourcing, and offshoring. Sharing information over computer networks is an effective way to overcome the obstacles of distance and time zone that accompany this approach. Unfortunately, the greater convenience provided by computer networks also brings with it major threats. Information security risks, such as leaks of information outside the company or loss of data due to the failure of computer systems, carry significant costs and consequences. In response, Yanmar has developed cnct-partner to provide a way of sharing information with partners with a high level of security that minimizes these risks.
2. Features of cnct-partner
The cnct-partner provides a means for the secure sharing of information between Yanmar and its partner organizations, including an online storage facility. A major feature of cnct-partner that minimizes security risks is that it protects information based on both the level of security management by the user and the importance of the information (“content”).
2.1. Access Rights
The cnct-partner controls access rights to files. System users are assigned access rights to files (“prohibited”, “read-only”, or “read, write, print”) based on the level of security management at the organization to which they belong (described in detail in section 2.3), the R&D project they are working on, and the importance of the information.
2.2. How Access Rights are Determined
While access rights are assigned to the members of R&D project teams, these alone do not determine the level of access available. Upper limits are also placed on access rights based on the level of security management at the organization to which they belong and the importance of the information. Use of information with low importance by users from organizations with a high level of security management is subject to minimal restrictions, allowing extensive use. On the other hand, use of information with high importance by users from organizations with a low level of security management is subject to restrictions on sharing to reduce risks.

2.3. Security Management Level
The level of security management is determined from the following two criteria.
- Country risk
- The extent of legal protection for intellectual property varies from country to country. This is taken into account when considering the risk of information leak associated with the country in which the user is based.
- Information leak risk
- Risk of information leak is assessed using a checklist that considers the applicable conditions based on the potential risks shown in the figure below.
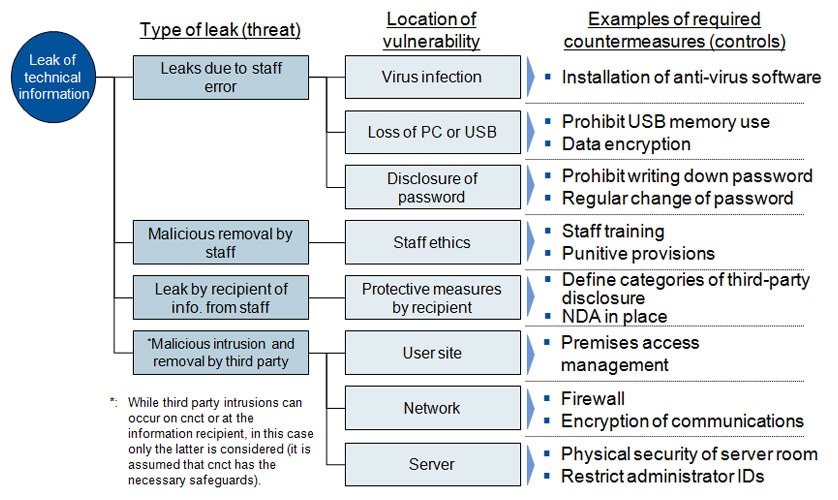
A security management level is assigned to user organizations based on the results of assessing this country risk and information leak risk.
3. Conclusions
Yanmar intends to deploy cnct-partner mainly at partner organizations involved in joint research or contract development. The security management features of cnct-partner described in this article mean that its use for file transfer reduces the risk of information leaks. As a revision history is maintained for files stored in cnct-partner, it can also be used to check for differences with files transferred in the past.
Use of cnct-partner allows Yanmar R&D staff to feel confident about the speedy exchange of important information with their many external partners. Yanmar believes this will also help expedite its R&D work.
-IMPORTANT-
The original technical report is written in Japanese.
This document was translated by R&D Management Division.
Author
