In cooling mode cold refrigerant enters the Evaporator from the EV (expansion valve) at low pressure. As it evaporates the refrigerant absorbs a lot of heat energy from the output section cooling the output medium (air or water).
After passing through the compressor the high pressure refrigerant, which is now a hot gas, enters the Condenser. As it condenses the refrigerant releases heat energy to the air source before flowing once again to the EV to repeat the cycle.
Gas-Engine Heat Pumps (GHP)
Overview
Yanmar Gas-engine Heat Pumps (GHP) provide very efficient gas powered heating and cooling solutions for all kinds of buildings. By using world class Yanmar gas-engines to drive the system, these reversible air-source heat pumps can give low running costs, reduce CO2 emissions and use very little electricity. GHP is a well established technology and Yanmar has been one of the leaders in this field for the last 30 years. By offering Air-to-air (VRF) and Air-to-water GHP systems, Yanmar can provide efficient and cost effective solutions for a wide range of cooling and heating applications.
Typical Applications for GHP Units

Yanmar GHP mechanism
Yanmar GHP systems are air source heat pumps that operate using vapour-compression cycles driven by Yanmar gas-engines. GHP heat pumps use renewable heat energy exchange with the outside air source to provide high efficiency cooling and heating outputs.
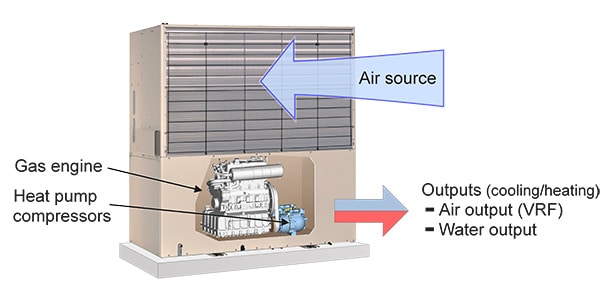
Yanmar provides heat pump solutions for both air and water output mediums to suit a wide range of customer applications.
Vapour-compression Cycle
The vapour compression cycle operates using the properties of refrigerant to transfer large amounts of heat energy at temperatures that are useful for cooling and heating applications. When refrigerant changes state from liquid to gas it absorbs a lot of heat energy which is released again in the change back to liquid. At high pressures this state changes occurs at high temperatures and at low pressures it occurs at low temperatures. In addition, the temperature of refrigerant can be raised by increasing its pressure or lowered by decreasing its pressure. These properties of refrigerant are used in a closed loop cycle operating in different modes exchanging heat energy with the air source to provide highly efficient cooling and heating all year round.
Cooling Mode

Heating Mode

In heating mode the refrigerant flow, Evaporator and Condenser are reversed. Now the refrigerant evaporates absorbing heat energy from the air source and condenses at the output section giving up heat to the output medium (air or water).

 Agriculture
Agriculture
 Tractor
Tractor
 Implements
Implements
 Combine Harvesters
Combine Harvesters
 Rice Transplanter
Rice Transplanter
 Sugarcane Harvesters
Sugarcane Harvesters
 Recreational Marine
Recreational Marine
 Marine Commercial
Marine Commercial
 Compact Power Products
Compact Power Products
 Compact Equipment
Compact Equipment
 Excavators
Excavators
 Attachments
Attachments
 Industrial Engine
Industrial Engine
 Energy Systems
Energy Systems
 Power Generation
Power Generation

